

These usually need to write system setting files that require administrative access and will prompt you for your password. Some Applications come in a package which are handled by the Macintosh Installer.
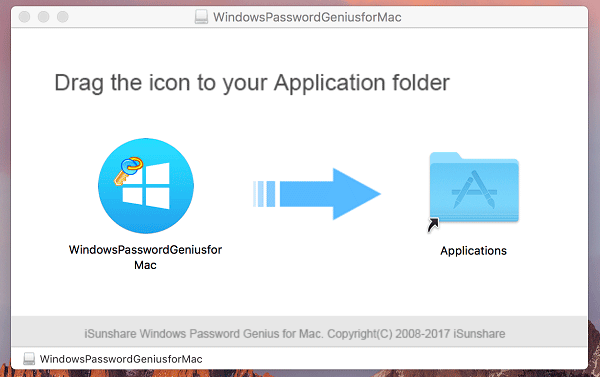
This is because most disk images are read-only, and running it from inside the disk image can produce undesirable results. When you download a disk image containing an Application, the app should be copied to your Applications folder before running it. They're important to a Mac as they contain metadata pertaining to the file itself. If you've ever copied a file from your Mac HD onto a FAT32 thumb drive, then plugged that drive into a Windows box and seen those pesky "._name" files, those are resource forks. These are called resource forks and are usually invisible to Mac users.

The DMG is a self contained volume formated HFS+ that retains file system attributes that are important.
WHAT ARE DMG FILES MAC MAC OS
You must always unmount a drive on the Mac OS before removing it, whether it be physical or virtual.Ī DMG is similar to any other compressed file, like ZIP in Windows, but more powerful on the Mac OS. When you "safely remove" it, you're unmounting it. This is similar to Windows in that when a removable drive is plugged it, it's automatically assigned a drive letter (E:). These volumes are "mounted" or "unmounted" on the Mac OS. This is one of the features that makes a Mac so powerful. You can clone one volume to another easily, whether it be physical or virtual. The hard drive icon you see on your desktop (probably Macintosh HD unless you renamed it) is a volume. Volumes on a Mac are basically any physical or virtual disk that can be mounted permanently or temporarily. These are treated like a Volume of their own, but one that's contained in that file.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
